Help us unlock the secrets of the brain! We want to study the role of a gene that connects the immune system to neurodevelopment to understand disorders such as schizophrenia.
What is the context of this investigation?
Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorders or schizophrenia, affect brain development and impact millions of people worldwide. These disorders arise from a combination of genetic and environmental factors that alter brain function early in life. Recent research highlights the involvement of the immune system and a little-studied gene (let’s call it the gene X) in brain development and function. However, the exact role of this gene in neurodevelopmental processes remains poorly understood, creating the need for further study.
How important is this project?
This project aims to fill a critical gap in our understanding of how "gene X" influences brain development. Disorders associated with neurodevelopment have a profound impact on individuals, families and society, but effective treatments remain limited due to incomplete knowledge of their underlying causes. By studying the function of the gene of interest, this research may reveal new therapeutic targets for the treatment of these disorders. In addition, a knockout cell line for "gene X" will be created, advancing methods for studying brain development in the laboratory.
What are the project objectives?
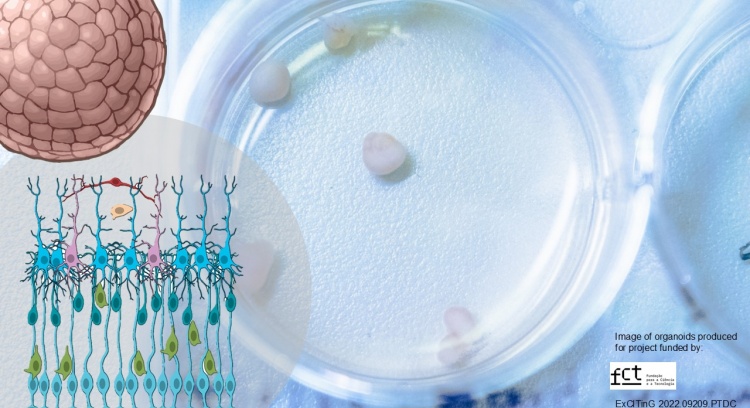
The main objective of this project is to understand how "gene X" inactivation affects neurodevelopment, using brain organoids derived from human stem cells.
We will use CRISPR/Cas9 technology to inactivate gene function in a line of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These cells will then be used to grow brain organoids, a 3D structure similar to embryonic brain tissue. By comparing organoids with and without the gene, we can examine the effect of "gene X" on changes in cellular composition and maturation, cortical layering, neuronal migration, and synaptic and dendritic structure. Finally, we will study global changes in gene expression to understand overall changes in cellular function.
About the author

Carolin no laboratorio
Dr Carolin Hoffmann developed a passion for bridging mental and physical health research during her studies at Maastricht University and Karolinska Institutet. This interest led her to specialise in neuroimmunology, focusing on how immune responses affect the brain in conditions such as psychosis and neurodevelopmental disorders.
During her PhD, Dr. Hoffmann investigated immunological markers in psychosis, gaining experience in antibody detection methods. She continued this work in the Netherlands and Spain, studying the impact of immune system alterations on brain health. Currently, at the University of Algarve, she leads research on the role of immune proteins (called the complement system) in psychiatric disorders. Advances in genetics and organoid technology motivate her efforts to discover the biological basis of these diseases.
With 15 scientific papers, presentations at international conferences and extensive experience in organizing scientific events, Dr. Hoffmann is well positioned to lead this project in collaboration with her colleagues at ABC-Ri.
For more information, see Dr. Hoffmann’s full CV [ https://www.cienciavitae.pt/211F-792C-1B73 ].

Ana no laboratorio
Ana Gomes is a Masters student in Biomedical Sciences at the University of Algarve, with a passion for understanding the mechanisms underlying mental health disorders. Her interest in neuroscience stemmed from personal experiences with mental health challenges and a desire to contribute to research in areas such as schizophrenia, a condition that affects millions worldwide.
During her undergraduate thesis, Ana collaborated with Dr. Carolin Hoffmann on a project investigating DNA methylation, a process that influences how genes are used during brain development. This work highlighted potential links between changes in DNA methylation and brain disorders such as autism and schizophrenia, inspiring her to explore these hidden mechanisms further. Ana aims to contribute to advances in the understanding and treatment of neuropsychiatric conditions and is excited to undertake the research described in this project as part of her master’s project.
Budget and due dates
All requested budget will be used for the acquisition of laboratory materials and sequencing services. We will use the CRISPR/CAS9 system to “eliminate” the gene of interest from the genome of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Since not all cells take up the plasmid, it is necessary to select the cells to obtain the correct “clones”. The result will be a hiPSC cell line with knockout of the specific gene. These cells will be used to grow cerebral organoids, using the STEMdiff™ Cerebral Organoid Kit followed by the maturation kit. We will use biomolecular methods to analyze the organoids, namely staining with fluorescent antibodies, observable under the microscope, and qPCR, to measure the expression of specific genes. Finally, we will use mRNA sequencing services to study changes in gene expression.
Material/Service
|
Material/Service
|
Price
|
|
Design and synthesis of sgRNAs and Cas9 plasmid
|
2500
|
|
Cell culture reagents
|
2277.5
|
|
Biomolecular analysis
|
2200
|
|
mRNA sequencing
|
2100
|
|
Platform fee
|
922.5
|
|
Total
|
10000
|
Timeline:
- Cloning: The project will start with the design and cloning of plasmid DNA for the CRISPR/CAS9 methodology, which will take about four months.
- Transfection: A human pluripotent stem cell line will be transfected to take up the engineered DNA, and the transfected clones will be selected and analyzed, which will take about three months. The result will be a knockout hiPSC line.
- Organoid Cultivation: The selected cell line will be used to culture brain organoids using the STEMdiff™ Cerebral Organoid Kit followed by the Maturation Kit. Multiple batches will be cultured, each taking 4 months to mature.
- Biomolecular analyses: We will use biomolecular methods to analyze the organoids, namely staining with fluorescent antibodies, observable under a microscope, and qPCR to measure the expression of specific genes. Finally, we will use mRNA sequencing services to study changes in gene expression.
- Publication of results: The results will be summarized in a manuscript and published in an open access scientific journal. The cost of publication, between 1000-5000 €, is not included in the budget, as funding is available through ABC-Ri and the municipality of Loulé.

Ana no laboratorio
Images